Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Face Markers and Surface Data#
Demonstrate the usage of several attributes of tetgen.TetGen.
You can access faces and edges from an instance of tetgen.TetGen from
the tetgen.TetGen.trifaces and tetgen.TetGen.edges attributes.
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import tetgen
First, let’s tetrahedralize a sphere.
sphere = pv.Icosphere(nsub=1)
tet = tetgen.TetGen(sphere)
tet.tetrahedralize(order=1, mindihedral=20, minratio=1.5, regionattrib=True)
tet.grid
Next, let’s construct a pyvista.PolyData from the triangular faces,
accessible from the tetgen.TetGen.trifaces attribute.
# mesh containing both exterior and interior elements
trimesh = pv.PolyData.from_regular_faces(tet.node, tet.trifaces)
trimesh
Interior faces are marked by the tetgen.TetGen.triface_markers attribute.
We can plot this using PyVista.
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(
trimesh.explode(0.3),
scalars=tet.triface_markers,
show_edges=True,
show_scalar_bar=False,
)
pl.enable_ssao(radius=0.1)
pl.enable_anti_aliasing("ssaa")
pl.camera.zoom(1.5)
pl.show()
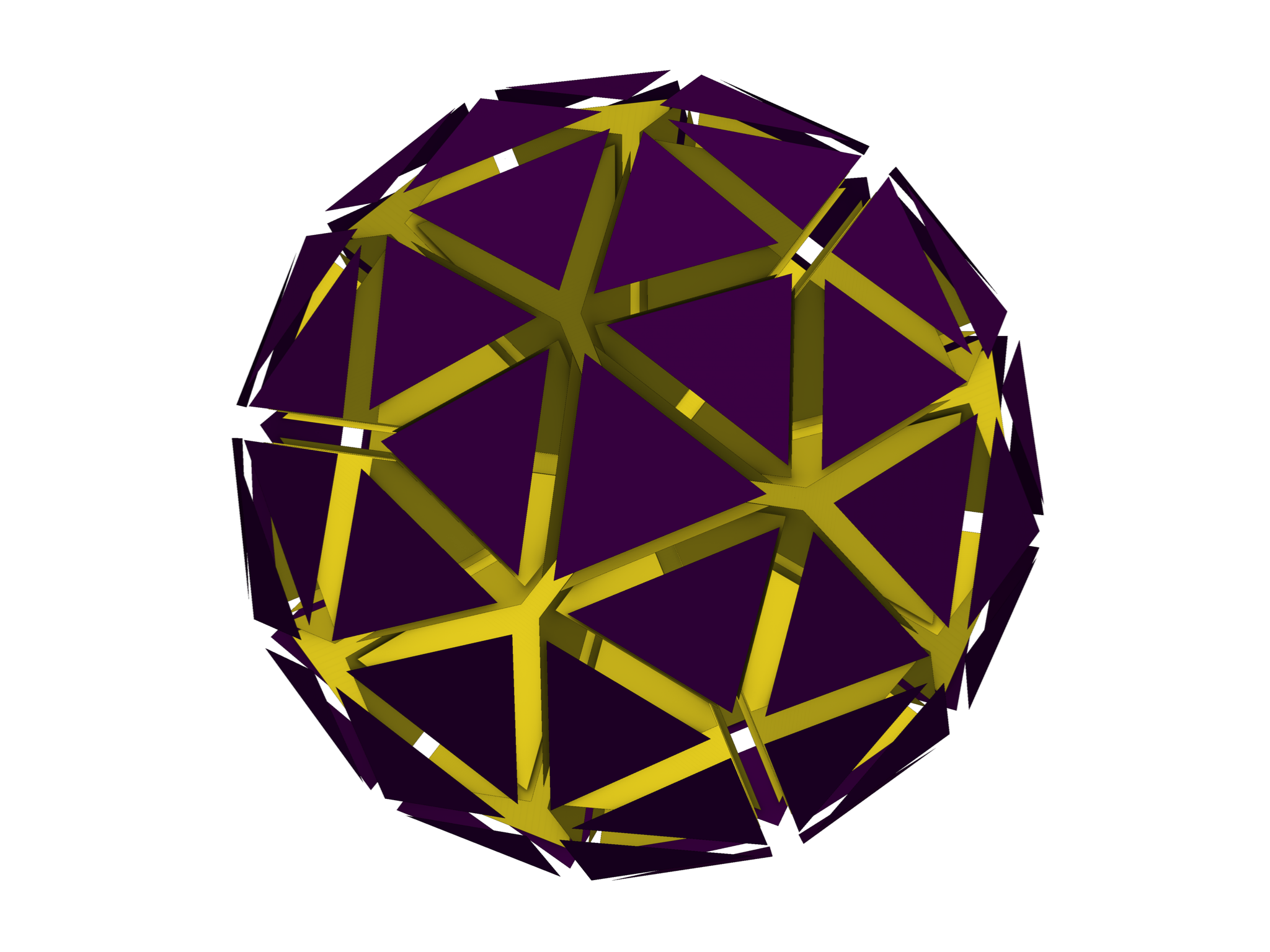
Interior faces are denoted with 0 and exterior faces are marked as -1 within
the tetgen.TetGen.triface_markers array.
tet.triface_markers
array([-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1], dtype=int32)
Finally, create an edges pyvista.PolyData from the
tetgen.TetGen.edges attribute.
# construct a VTK style edges array
n_edges = tet.edges.shape[0]
edges = np.empty((n_edges, 3), dtype=int)
edges[:, 0] = 2
edges[:, 1:] = tet.edges
# mesh containing both exterior and interior elements
edgemesh = pv.PolyData()
edgemesh.points = tet.node
edgemesh.lines = edges
edgemesh
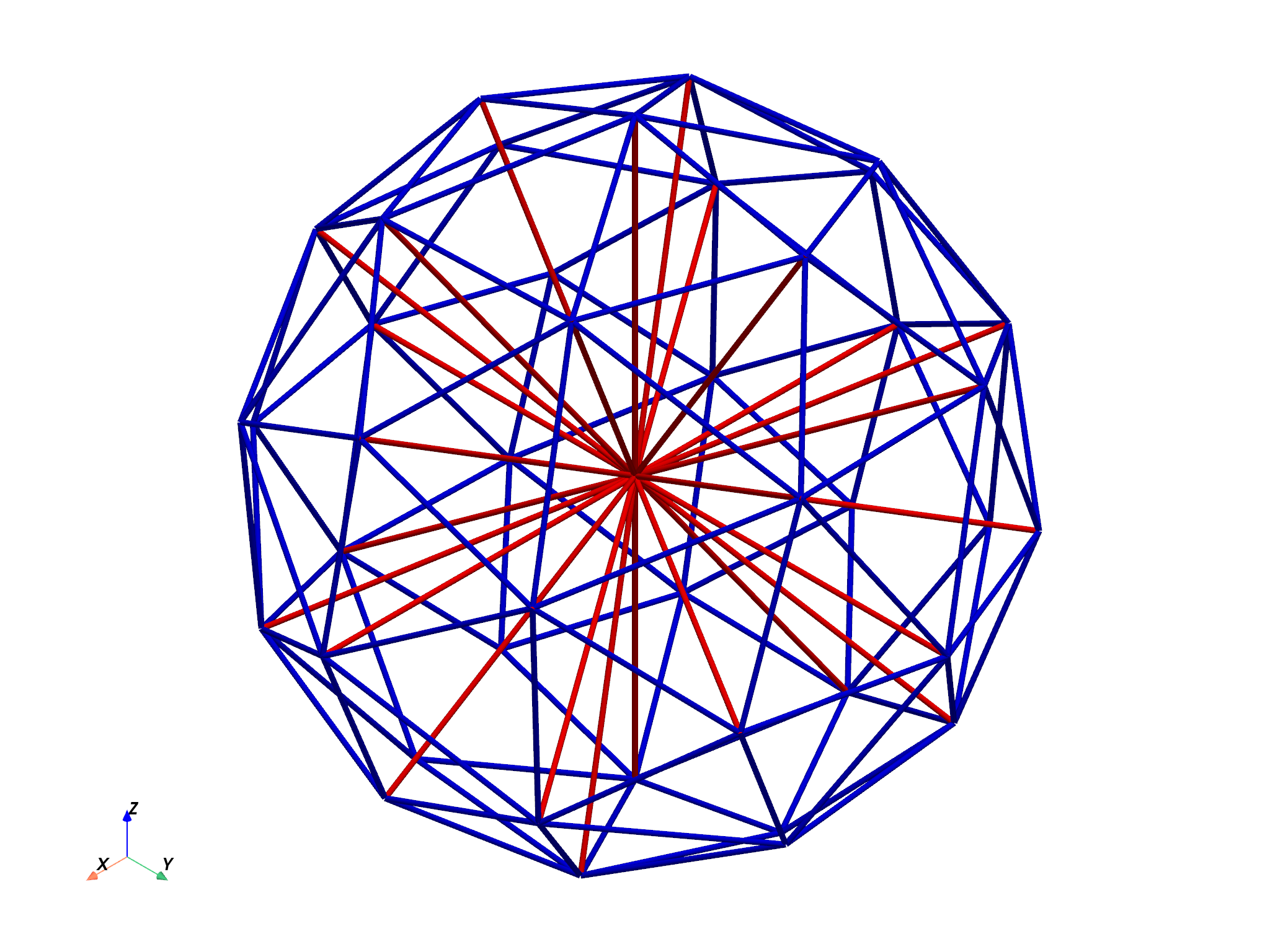
Plot the edges with pyvista and color the interior and exterior edges.
edgemesh.plot(
scalars=tet.edge_markers,
cmap="bwr",
line_width=10,
render_lines_as_tubes=True,
show_scalar_bar=False,
zoom=1.5,
)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.095 seconds)
